How to Install Reddit-like Fediverse Content Aggregator Kbin on Ubuntu 22.04
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Configure Firewall
- Step 2 - Install Git
- Step 3 - Install Nginx
- Step 4 - Install PHP and configure PHP
- Step 5 - Install Composer
- Step 6 - Install and Configure PostgreSQL
- Step 7 - Install Nodejs and Yarn
- Step 8 - Install Yarn
- Step 8 - Install Redis
- Step 9 - Install and Configure RabbitMQ
- Step 10 - Download Kbin
- Step 11 - Configure Environment File
- Step 12 - Install Kbin
- Step 13 - Install SSL
- Step 14 - Configure Nginx
- Step 15 - Install and Configure Supervisor
- Step 16 - Access Kbin
- Conclusion
Kbin is an open-source Reddit-like content aggregator and microblogging platform for the fediverse. It allows you to create and moderate communities and can communicate with other ActivityPub services including Mastodon, Pleroma, and Peertube.
While there are popular instances of Kbin you can join and use, you can run your own Kbin instance as well for your friends and family. In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Kbin on an Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Prerequisites
-
A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
-
A non-root sudo user.
-
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) like
example.com. -
Make sure everything is updated.
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt upgrade
-
Few packages that your system needs.
$ sudo apt install wget curl nano ufw software-properties-common dirmngr apt-transport-https gnupg2 ca-certificates lsb-release ubuntu-keyring unzip -y
Some of these packages may already be installed on your system.
-
Our installation also requires Access Control List(ACL) to work. Install it.
$ sudo apt install acl
Step 1 - Configure Firewall
The first step is to configure the firewall. Ubuntu comes with ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall) by default.
Check if the firewall is running.
$ sudo ufw status
You will get the following output.
Status: inactive
Allow SSH port so that the firewall doesn't break the current connection upon enabling it.
$ sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
Allow HTTP and HTTPS ports as well.
$ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https
Enable the Firewall
$ sudo ufw enable Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? y Firewall is active and enabled on system startup
Check the status of the firewall again.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see a similar output.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 - Install Git
Git is usually installed with the Ubuntu server but if it is not, you should install it using the following command.
$ sudo apt install git
Verify the installation.
$ git --version git version 2.34.1
Configure Git with basic information.
$ git config --global user.name "Your Name" $ git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
Step 3 - Install Nginx
Ubuntu ships with an older version of Nginx. To install the latest version, you need to download the official Nginx repository.
Import Nginx's signing key.
$ curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor \ | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
Add the repository for Nginx's stable version.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg arch=amd64] \
http://nginx.org/packages/ubuntu `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Update the system repositories.
$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
$ sudo apt install nginx
Verify the installation.
$ nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.24.0
Start the Nginx server.
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
Step 4 - Install PHP and configure PHP
Ubuntu 22.04 ships with PHP 8.1.2 version which is a bit outdated. We will install the latest PHP 8.2 version using Ondrej's PHP repository.
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Next, install PHP and its extensions required by Kbin.
$ sudo apt install php8.2-common php8.2-fpm php8.2-cli php8.2-amqp php8.2-pgsql php8.2-gd php8.2-curl php8.2-simplexml php8.2-dom php8.2-xml php8.2-redis php8.2-mbstring php8.2-intl unzip
Verify the installation.
$ php --version
PHP 8.2.7 (cli) (built: Jun 8 2023 15:27:40) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v4.2.7, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.2.7, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
Open the file /etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/www.conf.
$ sudo nano /etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
We need to set the Unix user/group of PHP processes to nginx. Find the user=www-data and group=www-data lines in the file and change them to nginx.
... ; Unix user/group of processes ; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group ; will be used. ; RPM: apache user chosen to provide access to the same directories as httpd user = nginx ; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir. group = nginx ...
Find the listen.owner = www-data and listen.group = www-data lines in the file and change them to nginx.
; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write ; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many ; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions. The owner ; and group can be specified either by name or by their numeric IDs. ; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user ; mode is set to 0660 listen.owner = nginx listen.group = nginx
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Increase the memory limit for PHP-FPM from 128 MB to 512 MB.
$ sudo sed -i 's/memory_limit = 128M/memory_limit = 512M/' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini
Increase the file upload size to 8 MB.
$ sudo sed -i 's/upload_max_filesize = 2M/upload_max_filesize = 8M/' /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.ini
Restart the PHP-FPM service.
$ sudo systemctl restart php8.2-fpm
Change the group of the PHP sessions directory to Nginx.
$ sudo chgrp -R nginx /var/lib/php/sessions
Step 5 - Install Composer
Composer is a dependency management tool for PHP and is required for Kbin installation. Grab the composer setup file.
$ php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
Run the installer to generate the Composer binary.
$ php composer-setup.php
Remove the setup file.
$ php -r "unlink('composer-setup.php');"
Move the composer.phar binary to the /usr/local/bin directory.
$ sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
Verify the Composer installation.
$ composer --version Composer version 2.5.8 2023-06-09 17:13:21
Step 6 - Install and Configure PostgreSQL
Ubuntu 22.04 ships with PostgreSQL 14 by default. We will be using PostgreSQL 15 instead.
Run the following command to add the PostgreSQL GPG key.
$ curl https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-key.gpg >/dev/null
Add the APT repository to your sources list.
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-key.gpg arch=amd64] http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'
Update the system repository.
$ sudo apt update
Now, you can install PostgreSQL using the command below.
$ sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
The postgresql-contrib package contains some extra utilities.
Check the status of the PostgreSQL service.
$ sudo systemctl status postgresql
? postgresql.service - PostgreSQL RDBMS
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/postgresql.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Sat 2023-06-17 09:15:50 UTC; 3h 40min ago
Main PID: 26989 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CPU: 1ms
Jun 17 09:15:50 nspeaks systemd[1]: Starting PostgreSQL RDBMS...
Jun 17 09:15:50 nspeaks systemd[1]: Finished PostgreSQL RDBMS.
You can see that the service is enabled and running by default.
Launch the PostgreSQL shell.
$ sudo -i -u postgres psql
Create the Kbin database.
postgres=# CREATE DATABASE kbin;
Create the Kbin user and choose a strong password.
postgres-# CREATE USER kbinuser WITH PASSWORD 'Your_Password';
Change the database owner to the Kbin user.
postgres-# ALTER DATABASE kbin OWNER TO kbinuser;
Exit the shell.
postgres-# \q
Verify that your credentials work.
$ psql --username kbinuser --password --host localhost kbin Password: psql (15.3 (Ubuntu 15.3-1.pgdg22.04+1)) SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off) Type "help" for help. kbin=>
Exit the shell by typing \q.
Step 7 - Install Nodejs and Yarn
Ubuntu 22.04 ships with Node v12 which is outdated. We will install the latest LTS version of Node which is v18 at the time of writing this tutorial.
Grab the Node v18 installer from NodeSource.
$ curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x -o nodesource_setup.sh
Run the installer script.
$ sudo bash nodesource_setup.sh
Install Node.js.
$ sudo apt install nodejs
Verify the Node.js version.
$ node -v v18.16.1
Delete the installer file.
$ rm nodesource_setup.sh
Step 8 - Install Yarn
Import the GPG key for Yarn.
$ curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg >/dev/null
Add the Yarn source to the system repositories list.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg] https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list
Update your system repositories list.
$ sudo apt update
Install Yarn
$ sudo apt install yarn
Verify the installation.
$ yarn --version 1.22.19
Step 8 - Install Redis
Magento uses Redis for session and cache storage. It is entirely optional and you can use the database for session storage. But Redis does a better job. The latest version of Magento works with Redis 7.0. Ubuntu ships with Redis 6.0 so we will use the Redis repository for installation.
Import the official Redis GPG key.
$ curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg
Add the APT repository to your sources list.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.list
Update the system repository list.
$ sudo apt update
Issue the following command to install the Redis server.
$ sudo apt install redis
Confirm the Redis version.
$ redis-server -v Redis server v=7.0.11 sha=00000000:0 malloc=jemalloc-5.2.1 bits=64 build=3af367a78d5e21e9
Let us verify the service connection by using the following command.
$ redis-cli
You will be switched to the Redis shell.
The first step is to set the password for the Redis default user. Replace Your_Redis_Password with a strong password of your choice. Make sure you prefix the password with the > character.
127.0.0.1:6379> acl setuser default >Your_Redis_Password
Test the Redis Authentication.
127.0.0.1:6379> AUTH Your_Redis_Password OK
Ping the service.
127.0.0.1:6379> ping PONG
Exit the service by typing exit.
If you want, you can use the following command to generate the Redis password.
$ openssl rand 60 | openssl base64 -A OaYOuq6J9HhxMV0sGCeZbaGecphCl4GBfVkCOPkNjkQE1FX9DKpGSCJcDb8UV+AuFKA8tR1PgjGequn1
Step 9 - Install and Configure RabbitMQ
Kbin requires RabbitMQ for message queuing purposes. We will install it from the Ubuntu repository.
$ sudo apt install rabbitmq-server
Create a Rabbit User. Choose a strong password.
$ sudo rabbitmqctl add_user kbin StrongPassword
Make the user an administrator.
$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags kbin administrator
Step 10 - Download Kbin
Before downloading Kbin, we need to create a Kbin user account.
$ adduser kbin
Add the kbin user to the sudo group.
$ sudo usermod -aG sudo kbin
Log in as the kbin user.
$ su - kbin
Create the /var/www/html/kbin directory.
$ sudo mkdir /var/wwww/html/kbin -p
Switch to the directory.
$ cd /var/www/html/kbin
Give proper permissions to the folder so that the currently logged-in user can perform tasks.
$ sudo chown $USER:$USER kbin
Clone the Kbin Git repository into the current folder. Make sure to add the period(.) at the end of the command to refer to the current folder.
$ git clone https://codeberg.org/Kbin/kbin-core.git .
Create the public/media directory.
$ mkdir public/media
Give full permission to it.
$ chmod 777 public/media
Step 11 - Configure Environment File
Generate the Mercure JWT secret key.
$ node -e "console.log(require('crypto').randomBytes(32).toString('hex'))"
Generate the App secret using the same command again.
$ node -e "console.log(require('crypto').randomBytes(32).toString('hex'))"
Create and open the .env file for editing in the Kbin directory.
$ nano .env
Paste the following code in it. Use the keys generated above in the following file.
# Run "composer dump-env prod" to compile .env files for production use (requires symfony/flex >=1.2). # https://symfony.com/doc/current/best_practices.html#use-environment-variables-for-infrastructure-configuration # kbin variables SERVER_NAME="nspeaks.xyz" # production KBIN_DOMAIN=nspeaks.xyz KBIN_TITLE=Howtoforge KBIN_DEFAULT_LANG=en KBIN_FEDERATION_ENABLED=true [email protected] [email protected] KBIN_JS_ENABLED=true KBIN_REGISTRATIONS_ENABLED=true KBIN_API_ITEMS_PER_PAGE=25 #KBIN_STORAGE_URL=/media KBIN_META_TITLE="Kbin Lab" KBIN_META_DESCRIPTION="content aggregator and micro-blogging platform for the fediverse" KBIN_META_KEYWORDS="kbin, content agregator, open source, fediverse" KBIN_HEADER_LOGO=false KBIN_CAPTCHA_ENABLED=false # Redis REDIS_PASSWORD=YourRedisPassword REDIS_DNS=redis://default:${REDIS_PASSWORD}@localhost:6379 ###> symfony/framework-bundle ### APP_ENV=prod APP_SECRET=427f5e2940e5b2472c1b44b2d06e0525 ###< symfony/framework-bundle ### ###> doctrine/doctrine-bundle ### # Format described at https://www.doctrine-project.org/projects/doctrine-dbal/en/latest/reference/configuration.html#connecting-using-a-url # IMPORTANT: You MUST configure your server version, either here or in config/packages/doctrine.yaml # POSTGRES_DB=kbin POSTGRES_USER=kbin POSTGRES_PASSWORD=Your_Password POSTGRES_VERSION=15 DATABASE_URL="postgresql://${POSTGRES_USER}:${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}@127.0.0.1:5432/${POSTGRES_DB}?serverVersion=${POSTGRES_VERSION}&charset=utf8" ###< doctrine/doctrine-bundle ### ###> symfony/messenger ### # Choose one of the transports below RABBITMQ_PASSWORD=RabbitMQPassword MESSENGER_TRANSPORT_DSN=amqp://kbin:${RABBITMQ_PASSWORD}@rabbitmq:5672/%2f/messages #MESSENGER_TRANSPORT_DSN=doctrine://default #MESSENGER_TRANSPORT_DSN=redis://${REDIS_PASSWORD}@redis:6379/messages ###< symfony/messenger ### ###> symfony/mailgun-mailer ### #MAILER_DSN=mailgun+smtp://[email protected]:key@default?region=us MAILER_DSN=smtp://AKIA3FIG4NVFH4TXXEXY:BJQvNI9U6JqSuUFQ9Ffd22Dvom/8KNwk7EIrFTRai02/@email-smtp.us-west-2.amazonaws.com:465 ###< symfony/mailgun-mailer ### ###> symfony/mercure-bundle ### # See https://symfony.com/doc/current/mercure.html#configuration # The URL of the Mercure hub, used by the app to publish updates (can be a local URL) MERCURE_URL=https://example.com/.well-known/mercure # The public URL of the Mercure hub, used by the browser to connect MERCURE_PUBLIC_URL=https://example.com/.well-known/mercure # The secret used to sign the JWTs MERCURE_JWT_SECRET="!ChangeThisMercureHubJWTSecretKey!" ###< symfony/mercure-bundle ### ###> symfony/lock ### LOCK_DSN=flock ###< symfony/lock ###
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Step 12 - Install Kbin
Install the packages required by Kbin using Composer.
$ composer install --prefer-dist --no-dev $ composer dump-env prod
Clear the cache.
$ APP_ENV=prod APP_DEBUG=0 php bin/console cache:clear $ composer clear-cache
Give proper permissions to the media folder.
$ sudo chown kbin:nginx public/media
Set proper file and directory permissions by using the setfacl command. The following command detects the current web server in use (Nginx) and sets permissions for the existing and future files and folders.
$ HTTPDUSER=$(ps axo user,comm | grep -E '[a]pache|[h]ttpd|[_]www|[w]ww-data|[n]ginx' | grep -v root | head -1 | cut -d\ -f1) $ sudo setfacl -dR -m u:"$HTTPDUSER":rwX -m u:$(whoami):rwX var $ sudo setfacl -R -m u:"$HTTPDUSER":rwX -m u:$(whoami):rwX var
Create and migrate the PostgreSQL database.
$ php bin/console doctrine:database:create $ php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate
You will be prompted if you want to continue with data migration. Type yes to proceed.
WARNING! You are about to execute a migration in database "kbin" that could result in schema changes and data loss. Are you sure you wish to continue? (yes/no) [yes]: > yes [notice] Migrating up to DoctrineMigrations\Version20230615203020 [notice] finished in 1373.9ms, used 24M memory, 79 migrations executed, 667 sql queries [OK] Successfully migrated to version : DoctrineMigrations\Version20230615203020
Install and build the public front end for the Kbin site.
$ yarn install $ yarn build
Create a new administrator user for Kbin.
$ php bin/console kbin:user:create username [email protected] password
Grant administrative privileges to the user.
$ php bin/console kbin:user:admin username
Update the Keys.
$ php bin/console kbin:ap:keys:update
Step 13 - Install SSL
We need to install Certbot to generate the SSL certificate. You can either install Certbot using Ubuntu's repository or grab the latest version using the Snapd tool. We will be using the Snapd version.
Ubuntu 22.04 comes with Snapd installed by default. Run the following commands to ensure that your version of Snapd is up to date.
$ sudo snap install core && sudo snap refresh core
Install Certbot.
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
Use the following command to ensure that the Certbot command can be run by creating a symbolic link to the /usr/bin directory.
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Run the following command to generate an SSL Certificate.
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d example.com
The above command will download a certificate to the /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com directory on your server.
Generate a Diffie-Hellman group certificate.
$ sudo openssl dhparam -dsaparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 4096
Check the Certbot renewal scheduler service.
$ sudo systemctl list-timers
You will find snap.certbot.renew.service as one of the services scheduled to run.
NEXT LEFT LAST PASSED UNIT ACTIVATES Wed 2023-06-28 10:09:00 UTC 20min left Wed 2023-06-28 09:39:00 UTC 9min ago phpsessionclean.timer phpsessionclean.service Wed 2023-06-28 11:13:02 UTC 1h 24min left Wed 2023-06-28 04:41:28 UTC 5h 7min ago ua-timer.timer ua-timer.service Wed 2023-06-28 12:11:00 UTC 2h 22min left n/a n/a snap.certbot.renew.timer snap.certbot.renew.service
Do a dry run of the process to check whether the SSL renewal is working fine.
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see no errors, you are all set. Your certificate will renew automatically.
Step 14 - Configure Nginx
Create and open the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/kbin.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/kbin.conf
Paste the following code in it.
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/kbin.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/kbin.error.log;
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384;
ssl_ecdh_curve X25519:prime256v1:secp384r1:secp521r1;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
# use https://blog.cloudflare.com/announcing-1111 Cloudfare+Apnic labs, It is free and secure
resolver 1.1.1.1 1.0.0.1 [2606:4700:4700::1111] [2606:4700:4700::1001] valid=300s;
root /var/www/html/kbin/public;
index index.php;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php;
}
# Pass PHP Scripts To FastCGI Server
location ~* \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock; # Depends On The PHP Version
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $realpath_root;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to writable files/directories
location ~* ^/sites/*/(documents|edi|era) {
deny all;
return 404;
}
# deny access to certain directories
location ~* ^/(contrib|tests) {
deny all;
return 404;
}
# Alternatively all access to these files can be denied
location ~* ^/(admin|setup|acl_setup|acl_upgrade|sl_convert|sql_upgrade|gacl/setup|ippf_upgrade|sql_patch)\.php {
deny all;
return 404;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
}
}
# enforce HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
Notice the root directory to be used in the Nginx configuration is /var/www/html/kbin/public/.
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted once finished.
Open the file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following line before the line include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;.
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Verify the Nginx configuration file syntax.
$ sudo nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Restart the Nginx service.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Step 15 - Install and Configure Supervisor
Supervisor is a process manager and we will use it as a process monitor for message worker (RabbitMQ) for Kbin. The first step is to install Supervisor.
$ sudo apt install supervisor
Create the /etc/supervisor/conf.d/messenger-worker.conf file and open it for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/supervisor/conf.d/messenger-worker.conf
Paste the following code in it.
[program:messenger-kbin] command=php /var/www/html/kbin/bin/console messenger:consume async --time-limit=3600 user=kbin numprocs=2 startsecs=0 autostart=true autorestart=true startretries=10 process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d stderr_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/%(program_name)s_stderr.log stderr_logfile_maxbytes=10MB stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/%(program_name)s_stdout.log stdout_logfile_maxbytes=10MB [program:messenger-ap] command=php /var/www/html/kbin/bin/console messenger:consume async_ap --time-limit=3600 user=kbin numprocs=2 startsecs=0 autostart=true autorestart=true startretries=10 process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d stderr_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/%(program_name)s_stderr.log stderr_logfile_maxbytes=10MB stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/%(program_name)s_stdout.log stdout_logfile_maxbytes=10MB
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Run the following commands to re-read and update the new configuration file.
$ sudo supervisorctl reread $ sudo supervisorctl update
Start all the Supervisor services.
$ sudo supervisorctl start all
Step 16 - Access Kbin
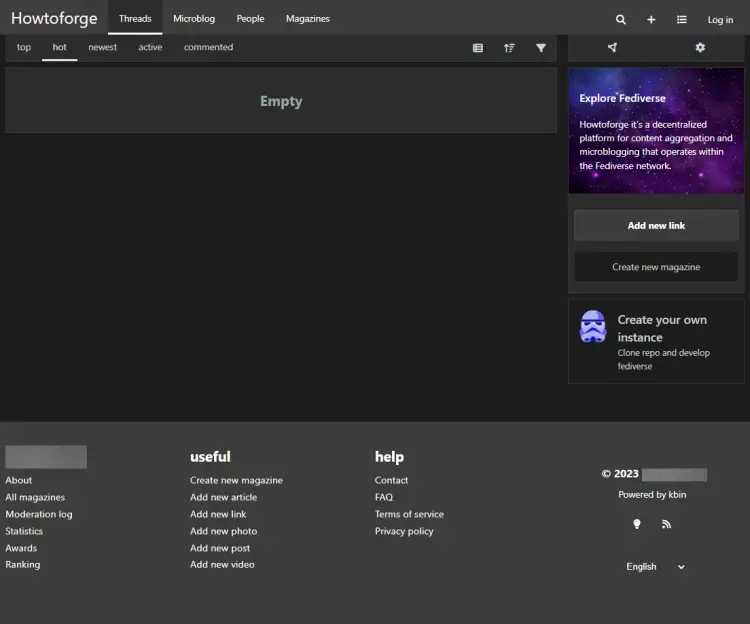
Open the URL https://example.com and you will get the following Kbin homepage.
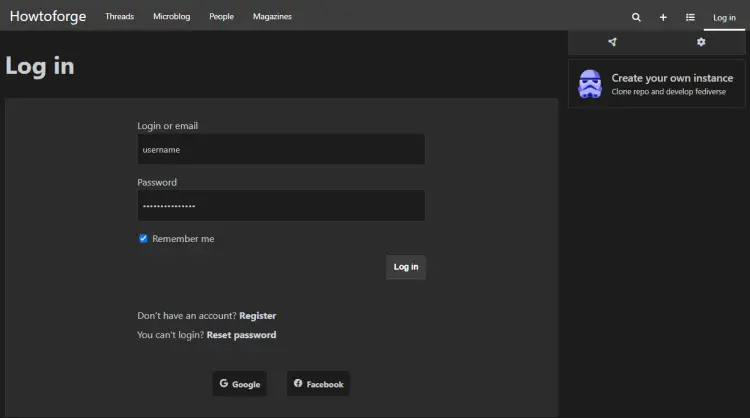
Click the Log in link at the top to bring up the login page.
Enter the credentials created in step 12 and click the Log in button to proceed. You will be taken back to the Kbin homepage. You can start using Kbin from hereon.
Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on installing Reddit-like Content Aggregator Kbin on a Ubuntu 22.04 server. If you have any questions, post them in the comments below.