How to Install and Create a Chat server using Matrix Synapse and Element on Debian 12
On this page
- Prerequisites
- Step 1 - Configure Firewall
- Step 2 - Install Matrix Synapse
- Step 3 - Install and Configure PostgreSQL
- Step 4 - Install Nginx
- Step 5 - Install SSL
- Step 6 - Configure Matrix Synapse
- Step 7 - Configure Nginx
- Step 8 - Install Coturn
- Step 9 - Access Matrix
- Step 10 - Install Element
- Step 11 - Configure Element
- Conclusion
Matrix is an open standard for decentralized and end-to-end encrypted communication. It is a collection of servers and services that communicate with each other using a standardized API that synchronizes in real time. It uses homeservers to store account information and chat history. If one homeserver goes down, other servers can continue communication without issues due to the nature of decentralization. You can either use a Matrix homeserver hosted by someone else or host your own to maintain control over your data.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install and create a chat server using Synapse, a homeserver implementation of Matrix. Element is a Matrix web client built using Matrix React SDK. This will allow you to offer Matrix chat on the web. You can also use the server using any other Matrix client of your choice. We will also be installing the Coturn server to enable Voice and Video calling. The Coturn service is optional in case you are not interested in using it.
Prerequisites
-
A server running Debian 12.
-
A non-sudo user with root privileges.
-
The uncomplicated Firewall(UFW) is enabled and running.
-
Fully Qualified Domain Names(FQDN) for Matrix, Element, and Coturn pointing to your server. We will be using
matrix.example.com,element.example.com, andcoturn.example.comrespectively for the three services. -
Ensure that everything is updated.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Step 1 - Configure Firewall
Before installing any packages, the first step is configuring the firewall to open ports for HTTP, HTTPS, and Synapse.
Check the status of the firewall.
$ sudo ufw status
You should see something like the following.
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Open the HTTP, HTTPS, and Synapse ports in the firewall.
$ sudo ufw allow 8448 $ sudo ufw allow http $ sudo ufw allow https
Check the status again to confirm.
$ sudo ufw status Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 ALLOW Anywhere 8448 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 8448 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Step 2 - Install Matrix Synapse
Add the Matrix GPG key.
$ sudo wget -O /usr/share/keyrings/matrix-org-archive-keyring.gpg https://packages.matrix.org/debian/matrix-org-archive-keyring.gpg
Add the Matrix APT repository.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/matrix-org-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.matrix.org/debian/ $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/matrix-org.list
Update the system repository list.
$ sudo apt update
Install Matrix Synapse.
$ sudo apt install matrix-synapse-py3
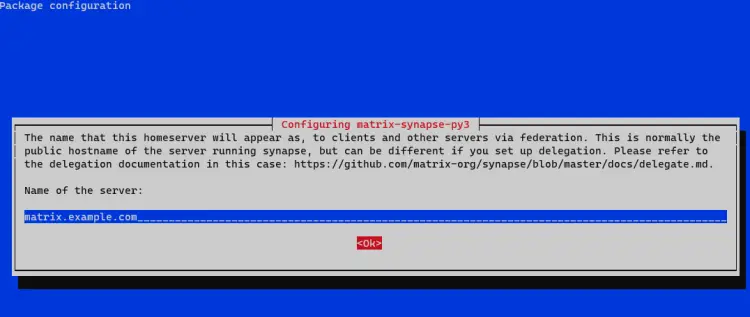
During the installation, you will be asked for the server name, which forms part of your Matrix ID. Enter your Matrix domain name in place of it. This will act as your homeserver address.
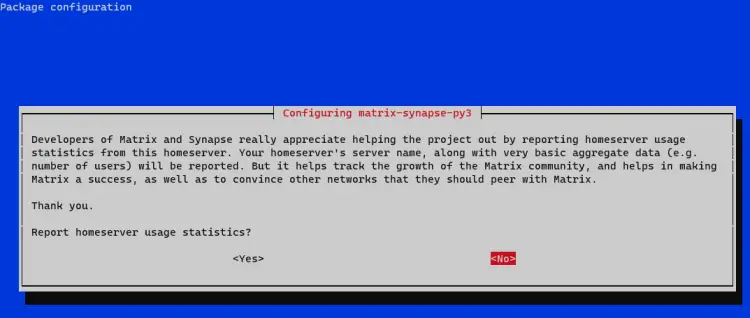
You will also be asked whether or not you wish to send anonymized statistics about your homeserver back to Matrix. Type N to refuse.
You can change these settings later in the file /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/server_name.yaml.
Matrix Synapse's service is enabled and started during installation. Check the status of the service.
$ sudo systemctl status matrix-synapse
? matrix-synapse.service - Synapse Matrix homeserver
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/matrix-synapse.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-10-02 07:47:43 UTC; 1min 33s ago
Process: 1558 ExecStartPre=/opt/venvs/matrix-synapse/bin/python -m synapse.app.homeserver --config-path=/etc/matrix-synapse/homeserver.yaml --config-path=/etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/ --generate-keys (code=>
Main PID: 1563 (python)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 2315)
Memory: 102.7M
CPU: 3.609s
CGroup: /system.slice/matrix-synapse.service
??1563 /opt/venvs/matrix-synapse/bin/python -m synapse.app.homeserver --config-path=/etc/matrix-synapse/homeserver.yaml --config-path=/etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/
Oct 02 07:47:41 lomp matrix-synapse[1558]: Generating signing key file /etc/matrix-synapse/homeserver.signing.key
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: This server is configured to use 'matrix.org' as its trusted key server via the
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: 'trusted_key_servers' config option. 'matrix.org' is a good choice for a key
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: server since it is long-lived, stable and trusted. However, some admins may
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: wish to use another server for this purpose.
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: To suppress this warning and continue using 'matrix.org', admins should set
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: 'suppress_key_server_warning' to 'true' in homeserver.yaml.
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp matrix-synapse[1563]: Config is missing macaroon_secret_key
Oct 02 07:47:43 lomp systemd[1]: Started matrix-synapse.service - Synapse Matrix homeserver.
Step 3 - Install and Configure PostgreSQL
We will use PostgreSQL's official APT repository to install the latest version of PostgreSQL. Run the following command to add the PostgreSQL GPG key.
$ curl https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-key.gpg >/dev/null
Add the APT repository to your sources list.
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/postgresql-key.gpg arch=amd64] http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'
Update the system repository.
$ sudo apt update
Now, you can install PostgreSQL using the following command.
$ sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
At the time of writing this tutorial, PostgreSQL 16 is the latest version. To install a different version, modify the command as follows which will install the PostgreSQL 14 instead.
$ sudo apt install postgresql-14 postgresql-contrib-14
Check the status of the PostgreSQL service.
$ sudo systemctl status postgresql
? postgresql.service - PostgreSQL RDBMS
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/postgresql.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2023-10-02 07:51:10 UTC; 13s ago
Main PID: 4001 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CPU: 1ms
Oct 02 07:51:10 lomp systemd[1]: Starting postgresql.service - PostgreSQL RDBMS...
Oct 02 07:51:10 lomp systemd[1]: Finished postgresql.service - PostgreSQL RDBMS.
You can see that the service is enabled and running by default.
Log in to the postgres system account.
$ sudo -su postgres
Create a new database user and a database for PostgreSQL.
$ createuser --pwprompt synapse $ createdb --encoding=UTF8 --locale=C --template=template0 --owner=synapse synapsedb
Exit the postgres account.
$ exit
Step 4 - Install Nginx
For the production environment, it is recommended to run the Synapse server using an Nginx proxy.
Debian 12 ships with an older version of Nginx. To install the latest version, you need to download the official Nginx repository.
Import Nginx's signing key.
$ curl https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key | gpg --dearmor \ | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg >/dev/null
Add the repository for Nginx's stable version.
$ echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nginx-archive-keyring.gpg] \
http://nginx.org/packages/debian `lsb_release -cs` nginx" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nginx.list
Update the system repositories.
$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
$ sudo apt install nginx
Verify the installation. Since we are using Debian, the following command needs to be run with sudo permission.
$ sudo nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.24.0
Start the Nginx server.
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
Check the status of the service.
$ sudo systemctl status nginx
? nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2023-10-02 07:59:12 UTC; 1s ago
Docs: https://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 5767 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5768 (nginx)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 2315)
Memory: 1.7M
CPU: 7ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??5768 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
??5769 "nginx: worker process"
Step 5 - Install SSL
We need to install Certbot to generate free SSL certificates offered by Let's Encrypt. You can either install Certbot using Debian's repository or grab the latest version using the Snapd tool. We will be using the Snapd version.
Debian 12 doesn't come with Snapd installed. Issue the following command to install Snapd.
$ sudo apt install snapd -y
Run the following commands to ensure that your version of Snapd is up to date.
$ sudo snap install core $ sudo snap refresh core
Install Certbot.
$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
Use the following command to ensure that the Certbot command can be run by creating a symbolic link to the /usr/bin directory.
$ sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
Check the Certbot version.
$ certbot --version certbot 2.6.0
Run the following command to generate an SSL Certificate.
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d matrix.example.com
The above command will download a certificate to the /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com directory on your server.
Generate a Diffie-Hellman group certificate.
$ sudo openssl dhparam -dsaparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 4096
Check the Certbot renewal scheduler service.
$ sudo systemctl list-timers
You will find snap.certbot.renew.service as one of the services scheduled to run.
NEXT LEFT LAST PASSED UNIT ACTIVATES ..... Mon 2023-10-02 16:33:00 UTC 8h left - - snap.certbot.renew.timer snap.certbot.renew.service Tue 2023-10-03 00:00:00 UTC 15h left - - dpkg-db-backup.timer dpkg-db-backup.service Tue 2023-10-03 00:00:00 UTC 15h left Mon 2023-10-02 07:38:16 UTC 26min ago exim4-base.timer exim4-base.service
Do a dry run of the process to check whether the SSL renewal is working fine.
$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see no errors, you are all set. Your certificate will renew automatically.
Step 6 - Configure Matrix Synapse
You can configure the Matrix server via the file /etc/matrix-synapse/homeserver.yaml but it is not recommended since it gets overwritten after every upgrade. For production use, you should place configuration files in the /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d folder.
Synapse's installation created two configuration files in the /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d folder.
$ ls /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d report_stats.yaml server_name.yaml
Create a new configuration file for the database and open it for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/database.yaml
Paste the following lines in the editor. Replace the your-password field with the PostgreSQL user password you created in step 3. Replace localhost with the IP address of your server, if you are hosting the database elsewhere.
database:
name: psycopg2
args:
user: synapse
password: 'your-password'
database: synapsedb
host: localhost
cp_min: 5
cp_max: 10
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Create a secret registration key. The key should be secured because it will allow anyone to register a new user, even if registration is disabled.
$ echo "registration_shared_secret: '$(cat /dev/urandom | tr -cd '[:alnum:]' | fold -w 256 | head -n 1)'" | sudo tee /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/registration_shared_secret.yaml registration_shared_secret: 'vgd73p26ZDaFExpX4OPv45DsA2ZMAxiVZR7um9fBoBoFESmg5MSs68xAMUhwQ8Zn3NqcZMRSqxLeIFatppfne7xD2RHL16YfuIKmNeJ1FClQszO1SZknUVwOPyDiPe5gCCWgD9cHfa3dLTdZND5Y0SdH7GBkwYqKjibAe0JoQc8mKty3HWd6uIga3QewhtXr3b3Hpk8sr6zYpXvaBtWRHwaSWcLooqbWF8LPbSyrC0BVAKzXObUwqRGyDpkrnMiY'
By default, Synapse enables presence indicators that show if a person is online. It can cause high CPU usage, therefore you can disable it. Create a new configuration file for the same.
$ sudo nano /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/presence.yaml
Paste the following line in the editor.
presence: enabled: false
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Restart the Synapse service to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart matrix-synapse
Create a new matrix user. You will be asked for your username and password. Since this is the first user we are creating, type yes when asked whether to make the user an administrator.
$ register_new_matrix_user -c /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/registration_shared_secret.yaml http://localhost:8008 New user localpart [navjot]: navjot Password: Confirm password: Make admin [no]: yes Sending registration request... Success!
If you want to open public registration, create a new configuration file.
$ sudo nano /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/registration.yaml
Paste the following lines in it.
enable_registration: true
By default, Synapse does not allow registrations without email verification. To enable email verification, paste the following lines.
registrations_require_3pid: - email email: smtp_host: mail.example.com smtp_port: 587 # If mail server has no authentication, skip these 2 lines smtp_user: '[email protected]' smtp_pass: 'password' # Optional, require encryption with STARTTLS require_transport_security: true app_name: 'HowtoForge Example Chat' # defines value for %(app)s in notif_from and email subject notif_from: "%(app)s <[email protected]>"
To disable email verification, paste the following line instead.
enable_registration_without_verification: true
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Restart Synapse to apply the configuration.
$ sudo systemctl restart matrix-synapse
Step 7 - Configure Nginx
Open the file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following line before the line include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;.
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Create and open the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/synapse.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/synapse.conf
Paste the following code in it.
# enforce HTTPS
server {
# Client port
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name matrix.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
server_name matrix.example.com;
# Client port
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# Federation port
listen 8448 ssl http2 default_server;
listen [::]:8448 ssl http2 default_server;
access_log /var/log/nginx/synapse.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/synapse.error.log;
# TLS configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:MozSSL:10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
resolver 1.1.1.1 1.0.0.1 [2606:4700:4700::1111] [2606:4700:4700::1001] 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 [2001:4860:4860::8888] [2001:4860:4860::8844] valid=60s;
resolver_timeout 2s;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384;
tcp_nopush on;
gzip on;
location ~ ^(/_matrix|/_synapse/client) {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8008;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
# Nginx by default only allows file uploads up to 1M in size
# Increase client_max_body_size to match max_upload_size defined in homeserver.yaml
client_max_body_size 50M;
}
}
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted once finished. The above configuration works on the assumption that the IP address of the domains example.com and matrix.example.com are pointing to the same server. If they are not, then use the following configuration file for the example.com server.
server {
server_name example.com;
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
# TLS configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/matrix.example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:MozSSL:10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
resolver 1.1.1.1 1.0.0.1 [2606:4700:4700::1111] [2606:4700:4700::1001] 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 [2001:4860:4860::8888] [2001:4860:4860::8844] valid=60s;
resolver_timeout 2s;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384;
# Redirect
location ~ ^(/_matrix|/_synapse/client) {
return 301 "https://matrix.example.com$request_uri";
}
# Client homeserver autodiscovery
location /.well-known/matrix/client {
default_type application/json;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
return 200 '{ "m.homeserver": { "base_url": "https://matrix.example.com" } }';
}
# Domain delegation
location /.well-known/matrix/server {
default_type application/json;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
return 200 '{ "m.server": "matrix.example.com" }';
}
}
Verify the Nginx configuration file syntax.
$ sudo nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Restart the Nginx service.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Step 8 - Install Coturn
You will need to install a Traversal Using Relays around the NAT (TURN) server to enable voice and video calling. For this purpose, we will install the Coturn package. If you don't need this functionality, you can skip this step.
Install Coturn.
$ sudo apt install coturn
Open the TURN and UDP ports.
$ sudo ufw allow 3478 $ sudo ufw allow 5349 $ sudo ufw allow 49152:65535/udp
Generate an SSL certificate for Turn (turn.example.com).
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d turn.example.com
Generate an authentication secret and save it in the configuration file.
$ echo "static-auth-secret=$(cat /dev/urandom | tr -cd '[:alnum:]' | fold -w 256 | head -n 1)" | sudo tee /etc/turnserver.conf static-auth-secret=OcKBLuwpE6IyMoi9mPccjVFaL7PwJRFUuKh5EvGBVcvB7tunevQ3cpP74we8cF4XSN8lFNrgqxJeyItKOcoOABwjdTNChmJeB4WMrsLV2JNsPs3U61s9rRijj3OxBpZux0CGft8CiyNDweVLqqxNaYphNesoAT4y51RxLVdAP2ros9S3jRR7IYRccJVRMpqTa8USBuBqAkzRRPLbFOHsC6QHur2oiySuW6sqs4YkH65N8kReSzgi7Fq2Zll3RO5e
Open the configuration file for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/turnserver.conf
Paste the following lines in it below the authentication secret.
use-auth-secret realm=turn.example.com cert=/etc/letsencrypt/live/turn.example.com/fullchain.pem pkey=/etc/letsencrypt/live/turn.example.com/privkey.pem # VoIP is UDP, no need for TCP no-tcp-relay # Do not allow traffic to private IP ranges no-multicast-peers denied-peer-ip=0.0.0.0-0.255.255.255 denied-peer-ip=10.0.0.0-10.255.255.255 denied-peer-ip=100.64.0.0-100.127.255.255 denied-peer-ip=127.0.0.0-127.255.255.255 denied-peer-ip=169.254.0.0-169.254.255.255 denied-peer-ip=172.16.0.0-172.31.255.255 denied-peer-ip=192.0.0.0-192.0.0.255 denied-peer-ip=192.0.2.0-192.0.2.255 denied-peer-ip=192.88.99.0-192.88.99.255 denied-peer-ip=192.168.0.0-192.168.255.255 denied-peer-ip=198.18.0.0-198.19.255.255 denied-peer-ip=198.51.100.0-198.51.100.255 denied-peer-ip=203.0.113.0-203.0.113.255 denied-peer-ip=240.0.0.0-255.255.255.255 denied-peer-ip=::1 denied-peer-ip=64:ff9b::-64:ff9b::ffff:ffff denied-peer-ip=::ffff:0.0.0.0-::ffff:255.255.255.255 denied-peer-ip=100::-100::ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff denied-peer-ip=2001::-2001:1ff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff denied-peer-ip=2002::-2002:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff denied-peer-ip=fc00::-fdff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff denied-peer-ip=fe80::-febf:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff # Limit number of sessions per user user-quota=12 # Limit total number of sessions total-quota=1200
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Restart Coturn to apply the configuration.
$ sudo systemctl restart coturn
Create a new Synapse configuration file for Coturn.
$ sudo nano /etc/matrix-synapse/conf.d/turn.yaml
Paste the following lines in it. Replace turn_shared_secret value with the value of static-auth-secret from the \etc\turnserver.conf file.
turn_uris: [ "turn:turn.example.com?transport=udp", "turn:turn.example.com?transport=tcp" ] turn_shared_secret: 'static-auth-secret' turn_user_lifetime: 86400000 turn_allow_guests: True
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Restart Synapse to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart matrix-synapse
Step 9 - Access Matrix
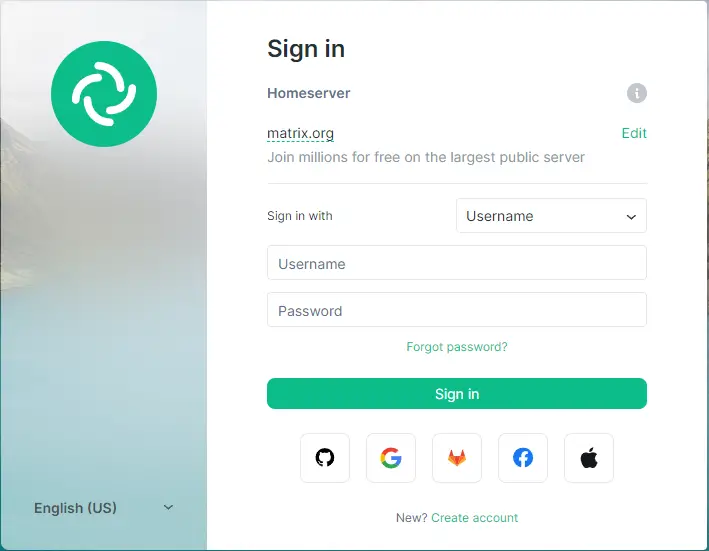
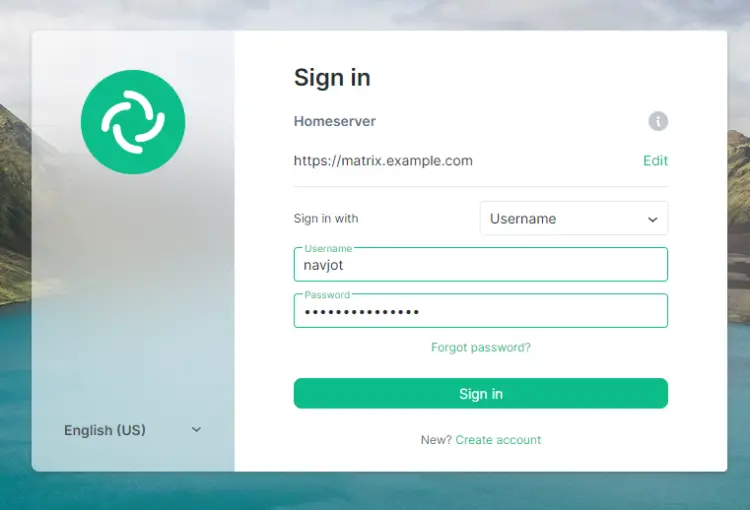
You can access Matrix Chat using Element's web client at https://app.element.io. Click the Sign in button to proceed.
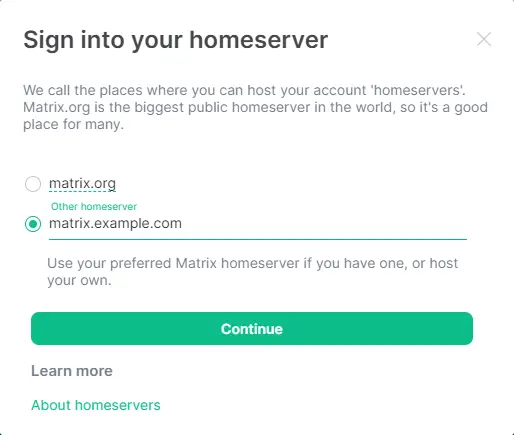
Click the Edit link under Homeserver. Enter matrix.example.com as your homeserver.
If the client detects your homeserver correctly, the boundary and the text will become green colored else it will be shown in red. Click Continue to proceed.
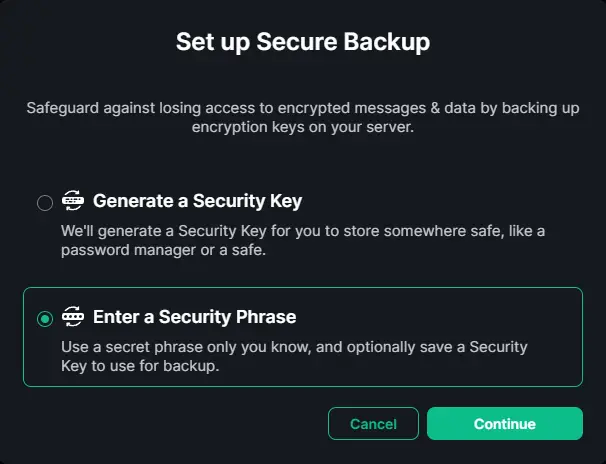
Click the Sign in button to log in. You will be asked to create a secure and encrypted backup.
Select the Enter a Security Phrase option to create a security phrase that will be required every time you log in. Click Continue to proceed.
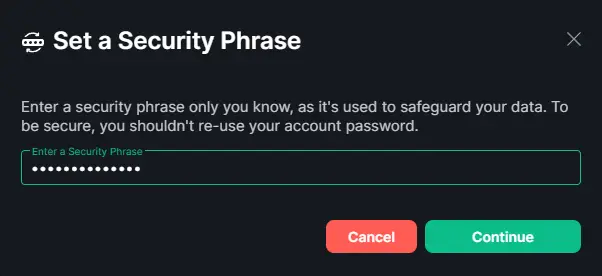
Enter a security phrase and click the Continue button to proceed. You will be asked to confirm it again on the next screen.
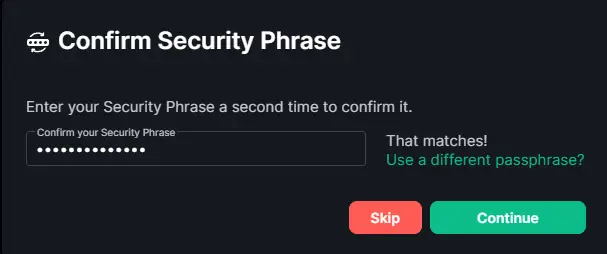
Enter the phrase again and click Continue to proceed.
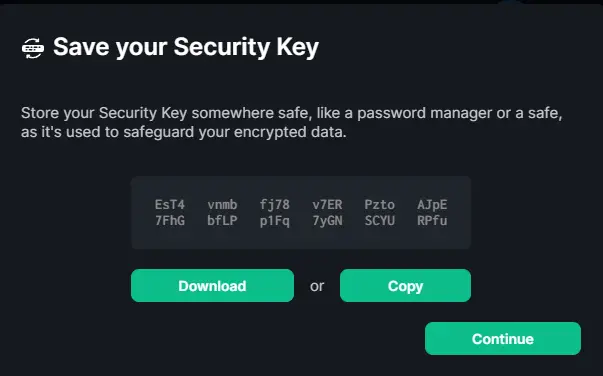
You will be given a set of security keys that you can use if you forget your security phrase. Click the Download button to save them.
Click the Continue button to proceed.
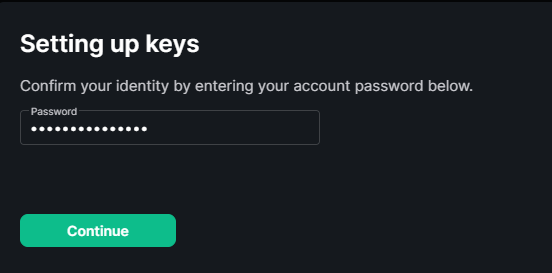
You will be asked for your account password. Enter the password and click the Continue button to finish setting up the encrypted backup.
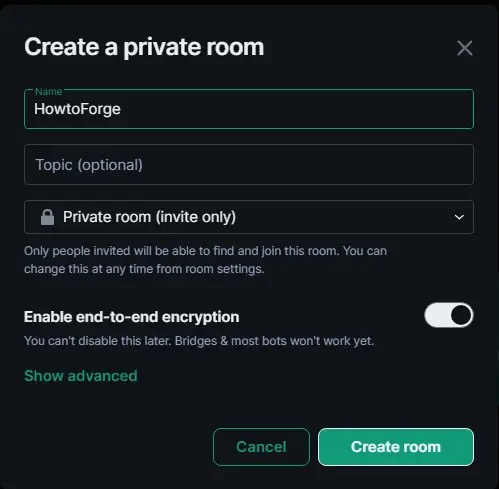
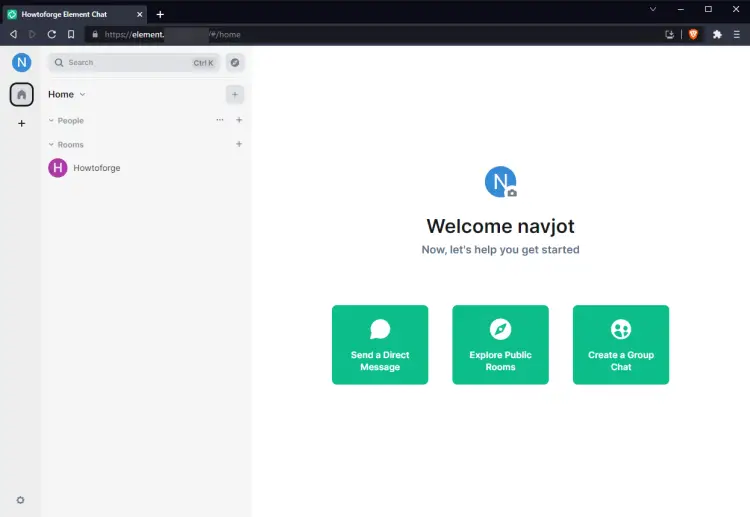
We created a group chat room named HowtoForge by using the Create a Group Chat button on the homepage. You will get the following popup when you click the button.
You can restrict members to the domain by expanding the advanced menu and selecting the option. Finish creating the room by clicking the Create room button.
Step 10 - Install Element
Install jq package to install JSON text processor. We will use it to grab the latest version of Element from its GitHub repository which doesn't need you to add the version numbers manually and allows you to update it using a single command.
$ sudo apt install jq
Create a directory for Element.
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/element
Create a new file for grabbing the latest Element release.
$ sudo nano /var/www/element/update.sh
Add the following lines to it.
#!/bin/sh
set -e
install_location="/var/www/element"
latest="$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/vector-im/element-web/releases/latest | jq -r .tag_name)"
cd "$install_location"
[ ! -d "archive" ] && mkdir -p "archive"
[ -d "archive/element-${latest}" ] && rm -r "archive/element-${latest}"
[ -f "archive/element-${latest}.tar.gz" ] && rm "archive/element-${latest}.tar.gz"
wget "https://github.com/vector-im/element-web/releases/download/${latest}/element-${latest}.tar.gz" -P "archive"
tar xf "archive/element-${latest}.tar.gz" -C "archive"
[ -L "${install_location}/current" ] && rm "${install_location}/current"
ln -sf "${install_location}/archive/element-${latest}" "${install_location}/current"
ln -sf "${install_location}/config.json" "${install_location}/current/config.json"
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Make the file executable.
$ sudo chmod +x /var/www/element/update.sh
Run the script to download Element.
$ sudo /var/www/element/update.sh
Step 11 - Configure Element
Copy the same element configuration file.
$ sudo cp /var/www/element/current/config.sample.json /var/www/element/config.json
Open the configuration file for editing.
$ sudo nano /var/www/element/config.json
Find the following lines.
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://matrix-client.matrix.org",
"server_name": "matrix.org"
},
Change the default Matrix homeserver address to your homeserver and remove the server_name variable.
"m.homeserver": {
"base_url": "https://matrix.example.com",
"server_name": "example.com"
},
If you want to use your name instead of Element in the website title, change the brand name.
"brand": "HowtoForge Example Chat",
Set the disable_guests variable as true to disallow Guests from using Element.
"disable_guests": true,
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Generate an SSL certificate for the Element client.
$ sudo certbot certonly --nginx --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staple-ocsp --preferred-challenges http -m [email protected] -d element.example.com
Create and open the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/element.conf for editing.
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/element.conf
Paste the following lines in it.
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name element.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name element.example.com;
root /var/www/element/current;
index index.html;
access_log /var/log/nginx/element.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/element.error.log;
add_header Referrer-Policy "strict-origin" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
# TLS configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/element.example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/element.example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/element.example.com/chain.pem;
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:MozSSL:10m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
ssl_dhparam /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem;
resolver 1.1.1.1 1.0.0.1 [2606:4700:4700::1111] [2606:4700:4700::1001] 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 [2001:4860:4860::8888] [2001:4860:4860::8844] valid=60s;
resolver_timeout 2s;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384;
}
Save the file by pressing Ctrl + X and entering Y when prompted.
Verify the Nginx configuration file syntax.
$ sudo nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Restart the Nginx service.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
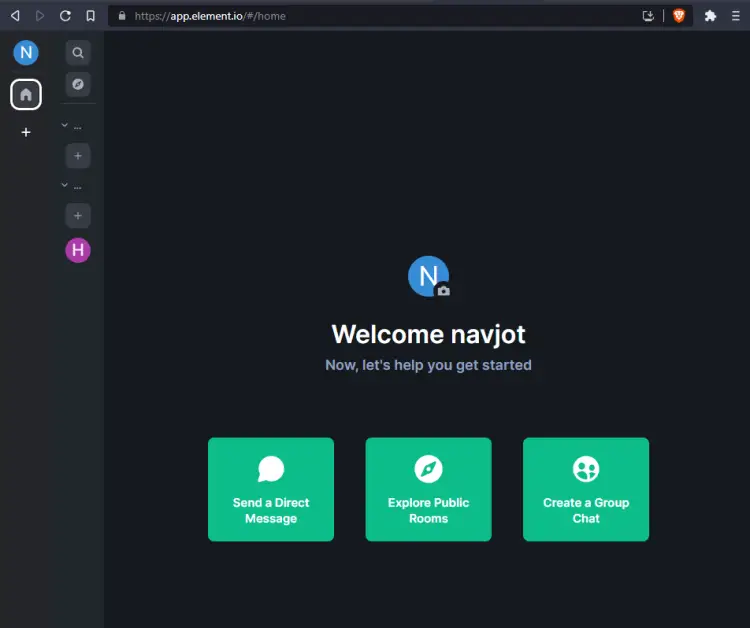
You can access the Element client via the URL https://element.example.com in your browser. Log in and you will be taken to the app dashboard. You will be asked to verify the app with the https://app.element.io first. Make sure you are logged in at the original Element app and you will be asked to match the emoji characters. Once you are verified, you will get the following dashboard.
Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on installing the Matrix Synapse Chat server along with Coturn and Element web client using Nginx as a proxy server on a Debian 12 machine. If you have any questions, post them in the comments below.